引言 从一个经典的链表 应用场景:LRU 缓存淘汰算法 说开去。
缓存 是为了解决高低速存储之间的差距而引入的技术。
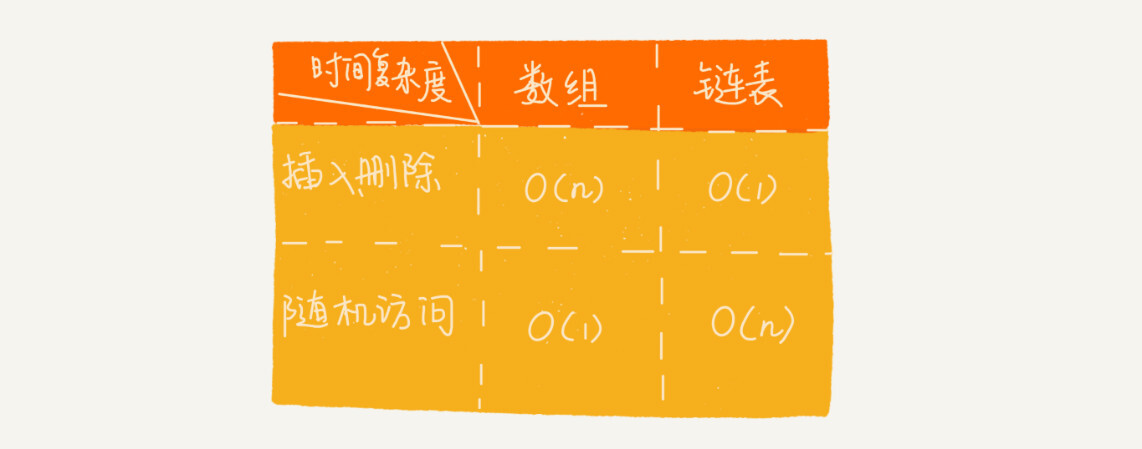
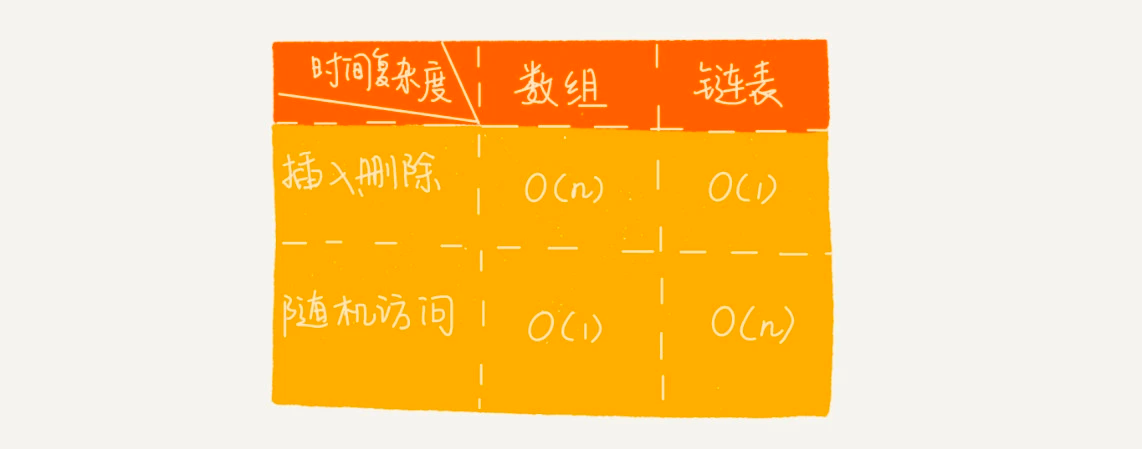
链表和数组对比:
缓存的大小有限,当缓存被打满的时候,就需要清理或者保留某些数据 ,这一部分就需要缓存淘汰策略来决定。
常见的策略有三种:
先进先出策略 FIFO (First In, First Out) 最少使用策略(Least Frequently Used) 最近最少使用策略(Least Recently Used) 这些策略就和我们清理房间采取的策略一致
那么如何采用 链表 ,来实现 LRU缓存淘汰策略 呢 ?
链表简介 首先解释一个 链表 的数据结构
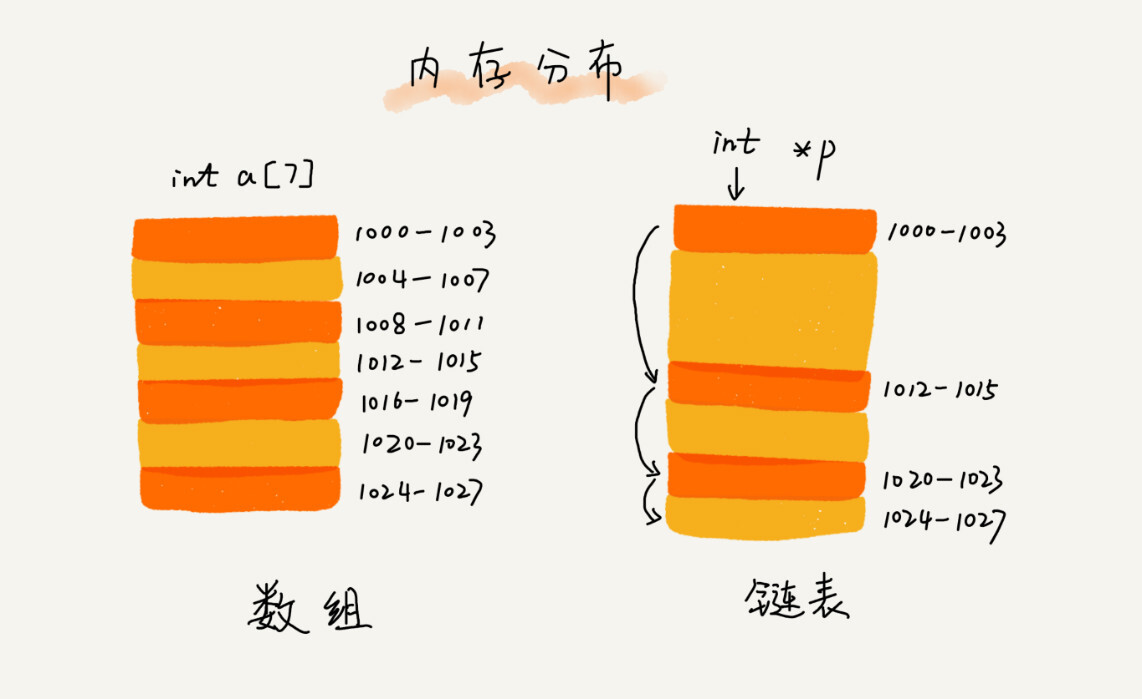
与数组结构不同的是,链表不需要连续的内存空间来存储 ,它是通过指针将一组零散的内存块串联起来使用 。
用一张图直观的解释:
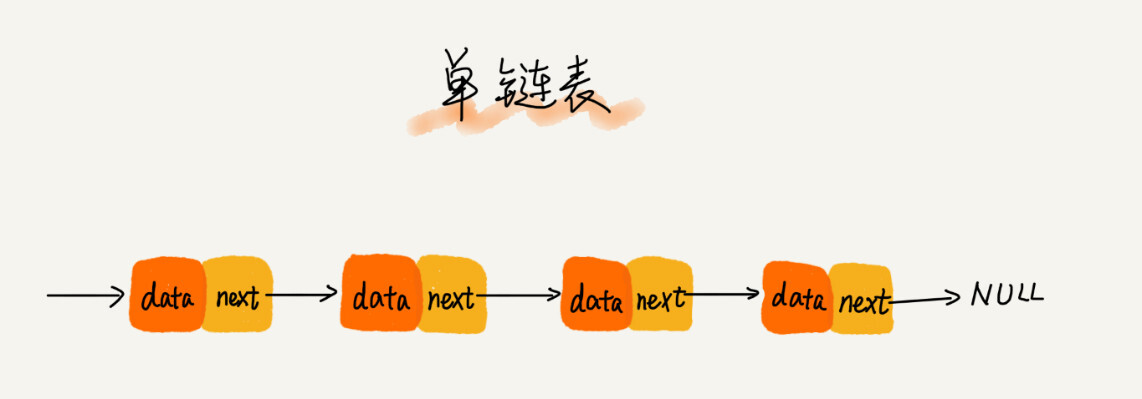
单链表
单链表 是通过一个个节点(Node) 组成的,每个节点包含了两个部分:
存储数据的 data 存储指针的next, 用于指向下一个 node 特点:
数据的插入 和删除 非常迅速(无序)—— 时间复杂度 O(1) 数据的查找 时间复杂度是 O(n)
单链表的实现 查找 - find() 删除 - remove() 链表元素添加头部添加元素 - add 尾部添加元素 - append 插入某个元素 - insert 链表元素展示 - traverse() 链表长度 - __len__ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 class Node (object def __init__ (self, data ): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList (object """ 单链表的实现 """ def __init__ (self ): self.head = None def find (self, data ): cur = self.head if cur is None : return -1 while cur != None : cur_data = cur.data if cur_data == data: return True cur = cur.next def remove (self, data ): cur = self.head pre = None if cur is None : return -1 while cur != None : if cur.data == data: if cur == self.head: self.head = self.head.next return pre.next = cur.next pre = cur cur = cur.next def add (self, data ): node = Node(data) node.next = self.head self.head = node def append (self, data ): node = Node(data) cur = self.head if cur is None : self.head = node return while cur.next != None : cur = cur.next cur.next = node def insert (self, index, data ): if index < 0 : self.add(data) elif index > self.__len__(): self.append(data) else : cur = self.head for i in range (index -1 ): cur = cur.next node = Node(data) node.next = cur.next cur.next = node def traverse (self ): cur = self.head while cur != None : print (cur.data, end='-***-' ) cur = cur.next print () def __len__ (self ): count = 0 cur = self.head while cur != None : count += 1 cur = cur.next return count if __name__ == '__main__' : items = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ] chain = LinkedList() for value in items: node = Node(value) chain.append(value) chain.traverse() chain.append(6 ) chain.traverse() chain.remove(3 ) chain.remove(5 ) chain.traverse() chain.insert(1 , 100 ) chain.traverse() print (chain.find(5 ), chain.find(1 )) print (len (chain))
循环链表 循环链表是一种特殊的单链表。它和单链表的唯一区别就是在尾节点 。循环链表的尾结点指针指向链表的头节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 class CircleLink (SingleChain ): def __init__ (self ): super (CircleLink, self).__init__() self._head = None def add (self, data ): node = Node(data) if self._head is None : node.next = node self._head = node else : cur = self._head while cur.next != self._head: cur = cur.next node.next = self._head self._head = node cur.next = node def append (self, data ): node = Node(data) if self._head is None : node.next = self._head self._head = node else : cur = self._head while cur.next != self._head: cur = cur.next node.next = self._head cur.next = node def travel (self ): cur = self._head while cur.next != self._head: print ("-**{}" .format (cur.data), end='' ) cur = cur.next print ("-**{}" .format (cur.data), end='' ) print () def find (self, data ): if self._head is None : return False cur = self._head index = 0 while cur.next != self._head: if cur.data == data: return index index += 1 cur = cur.next if cur.data == data: return self.__len__() return False def remove (self, data ): cur = self._head if cur.next == self._head: self._head = None return pre = None while cur.next != self._head: if cur.data == data: pre.next = cur.next return pre = cur cur = cur.next if cur.data == data: pre.next = self._head return def __len__ (self ): count = 0 cur = self._head while cur.next != self._head: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count + 1
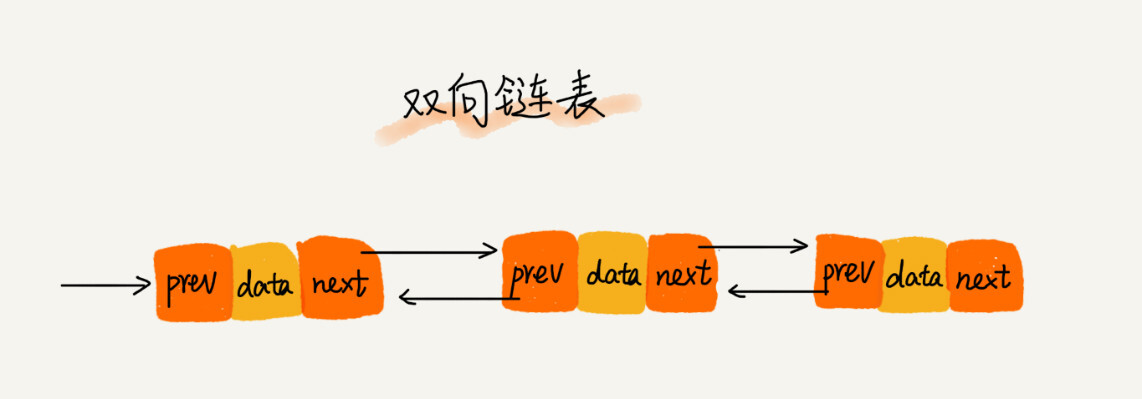
双向链表 双向链表,顾名思义,它支持两个方向,每个节点分为三个部分:
双向链表可以支持 O(1) 时间复杂度的情况下找到前驱节点,双向链表在某些情况下的 插入、删除等操作都要比单链表简单、高效。
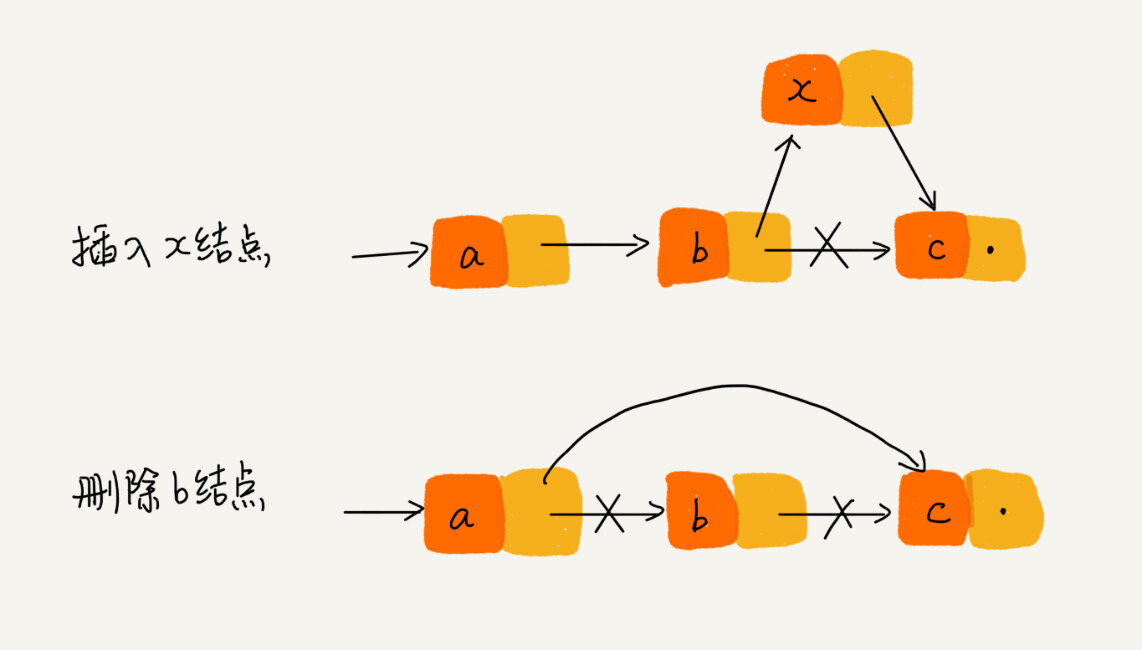
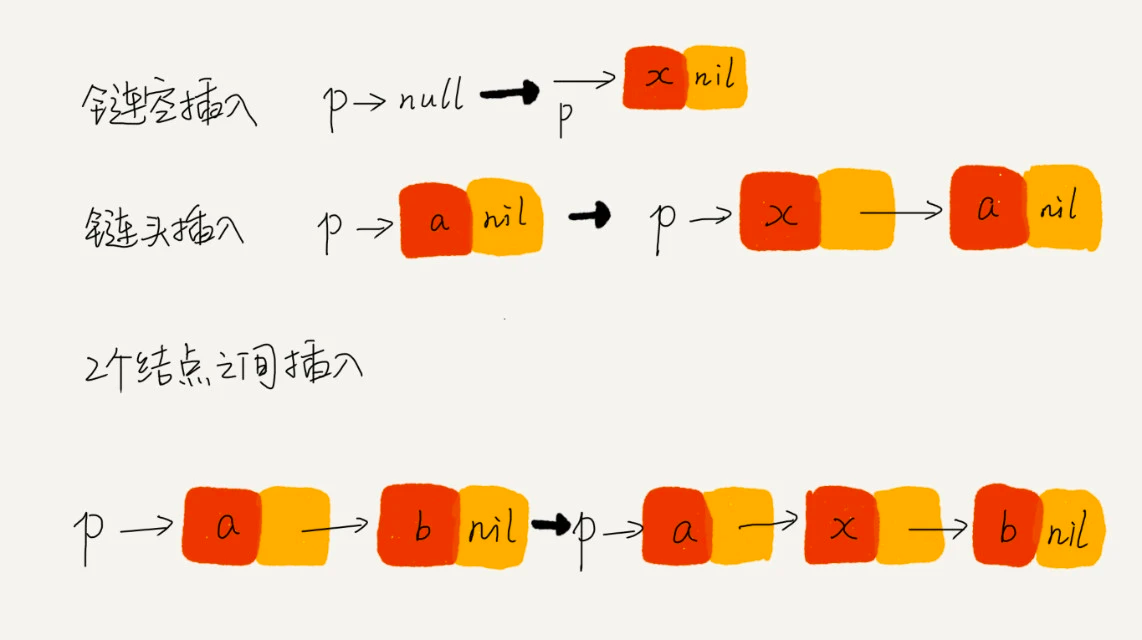
删除操作 删除节点中“值等于某个给定值” 的节点
对于这种情况,不管是单链表还是双链表,为了查找到值等于给定值的节点,都需要从头节点开始一个个依次遍历对比,找到后删除,时间复杂度为 O(n)
删除给定指针指向的节点
对于单链表来说,删除指定的节点时,还需要知道前驱节点,那么就会存在遍历的操作,时间复杂度为 O(n)。
对于双向链表来说,是存在 prev 指针的,那么时间复杂度相对于是 O(1)
插入操作 对于在某个节点前插入指定节点,时间复杂度是 O(1) 查询 对于一个有序链表来说,双向链表可以通过记录上次查找的位置 pos,根据要查找的值与 p 的大小关系,决定是往前还是往后查找,平均时间复杂度为 O(log(n))
双向链表实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 from chain.single_chain import SingleChainclass XNode (object def __init__ (self, data ): self.data = data self.prev = None self.next = None """ Author: tyrone File: 双向链表.py Time: 2023/3/20 """ class Node (object def __init__ (self, value ): self.prev = None self.next = None self.value = value class DoublyChain (object def __init__ (self ): self.head = None self.length = 0 self.history = (0 , None ) def append (self, value ): cur = self.head node = Node(value) if cur is None : self.head = node else : while cur.next : cur = cur.next cur.next = node node.prev = cur self.length += 1 def add (self, value ): cur = self.head node = Node(value) if cur is None : self.head = node else : node.next = self.head self.head.prev = node self.head = node self.length += 1 def insert (self, index, value ): if index <= 0 : self.add(value) elif index > self.length - 1 : self.append(value) else : cur = self.head count = 0 while count < index: cur = cur.next count += 1 node = Node(value) prev = cur.prev prev = cur.prev prev.next = node node.prev = prev node.next = cur cur.prev = node self.length += 1 def find (self, value ): cur = self.head count = 0 if cur is None : return -1 else : while cur.next : cur = cur.next count += 1 if cur.value == value: return count def travel (self ): cur = self.head while cur: print (cur.value) cur = cur.next if __name__ == '__main__' : double_chain = DoublyChain() double_chain.append(1 ) double_chain.append(2 ) double_chain.append(3 ) double_chain.insert(-1 , -1 ) double_chain.insert(100 , 100 ) double_chain.insert(2 , 20000 ) double_chain.insert(4 , 40000 ) cur = double_chain.head while cur: print (cur.value) cur = cur.next print (double_chain.find(40000 ))
总结 链表包括:
和数组相比,链表存储的数据是不连续的存储空间,数据之间采用指针引用方式连接。
链表实现注意点 链表为空的时候 链表只包含一个节点的情况 链表只包含头尾节点 举例绘图,辅助思考 思考题 LRU 的实现?
字符串是通过单链表来存储的,那如何判断一个回文字符呢?
解决思路:
法一:
使用快慢指针找到中点,然后将后半链表 reversed,然后一个指针在头部,一个指针在中部,逐个比较。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 def is_palindrome (head ) -> bool : if not head: return False if head.next == None : return True slow = reverse_node(find_middle_node(head)) traverse(slow) traverse(head) while slow: if head.data != slow.data: return False slow = slow.next head = head.next return True def find_middle_node (head ): fast, slow = head, head while fast.next and fast.next .next : fast = fast.next .next slow = slow.next return slow def reverse_node (head ): p, rev = head, None while p: rev, rev.next , p = p, rev, p.next return rev def traverse (node ): cur = node while cur != None : print (cur.data, end='-***-' ) cur = cur.next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : my_str = "1012101" c = Chain() for v in my_str: c.append(v) print (is_palindrome(c.head))
链表练习题目 反转链表 206 - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution : def reverseList (self, head: ListNode ) -> ListNode: res, p = None , head while p: res, res.next , p = p, res, p.next return res
环状链表判断 解题思路:使用快慢指针,如果两个指针相遇了说明是环状链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution : def hasCycle (self, head: Optional [ListNode] ) -> bool : if head == None : return False i = head j = head while j != None and j.next != None : i = i.next j = j.next .next if i == j: return True return False
合并两个有序链表 21 - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution : def mergeTwoLists (self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode ) -> ListNode: if l1 and l2: if l1.val > l2.val: l1, l2 = l2, l1 l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next , l2) return l1 or l2
删除链表的到处第 N 个节点 19 - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class ListNode : def __init__ (self, val=0 , next =None ): self.data = data self.next = None def removeNthFromEnd (head: ListNode, n: int ) -> ListNode: def getLength (head: ListNode ) -> int : length = 0 while head: length += 1 head = head.next return length dummy = ListNode(0 , head) length = getLength(head) cur = dummy for i in range (1 , length - n + 1 ): cur = cur.next cur.next = cur.next .next return dummy.next
876 - https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution : def middleNode (self, head: ListNode ) -> ListNode: n, cur = 0 , head while cur: n += 1 cur = cur.next k, cur = 0 , head while k < n // 2 : k += 1 cur = cur.next return cur
链表实现源码 https://github.com/tyronemaxi/algorithm/tree/main/chain